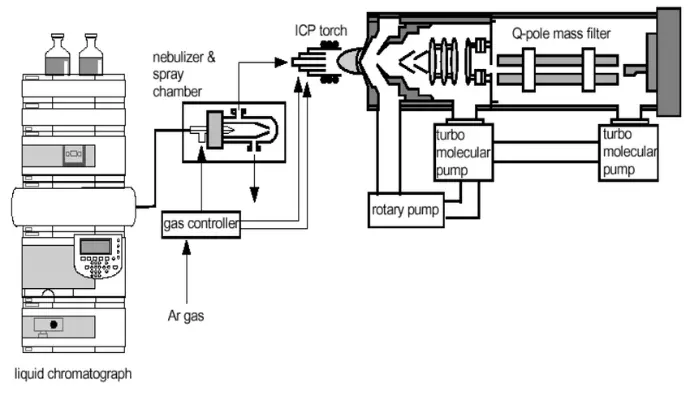
What is HPLC?
Understanding the Basics of Chromatography
Pharmaceutical Research and Medicine
Ensures drug purity, stability testing, and quality control in medicine development.


Environmental Monitoring
Analyzes pollutants in water, soil, and air to protect ecosystems and public health.

Why HPLC Matters (Applications & Impact):
HPLC is not only a routine technique in analytical chemistry but also a cornerstone of modern science and industry:
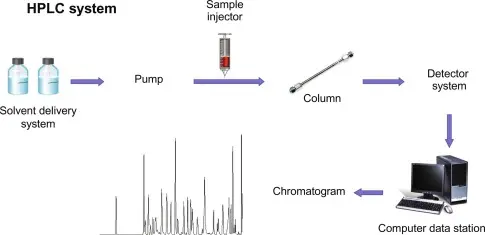
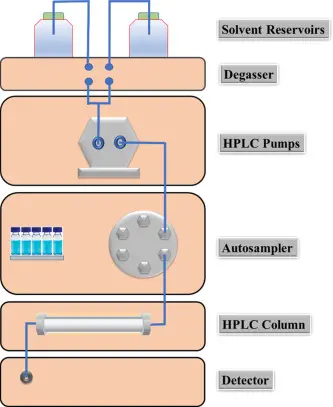
HPLC Techniques and Methods
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a cornerstone technique in analytical chemistry, widely used in research, pharmaceuticals, food safety, and environmental monitoring. To master HPLC, students and young researchers must understand not only the principles but also the different techniques, methods, and troubleshooting strategies that make the system reliable and precise.
Sample Preparation Techniques
Proper sample preparation is critical to ensure reproducible and accurate results.Read more
Common methods include:
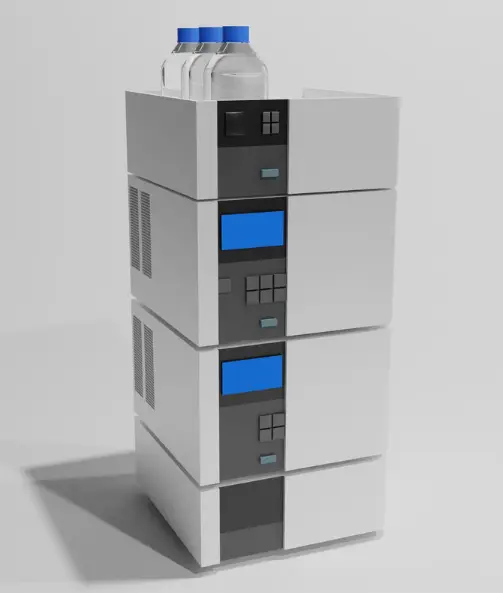





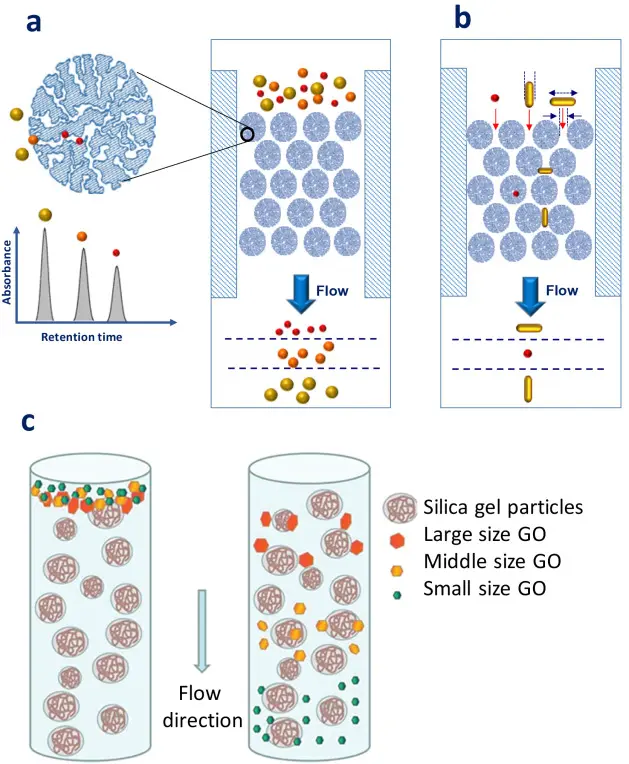
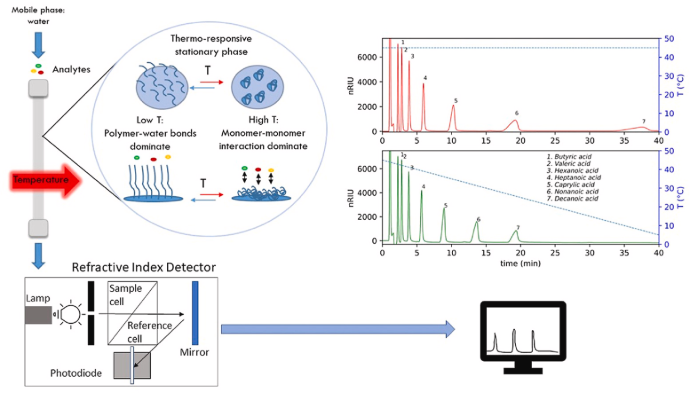
Types of HPLC
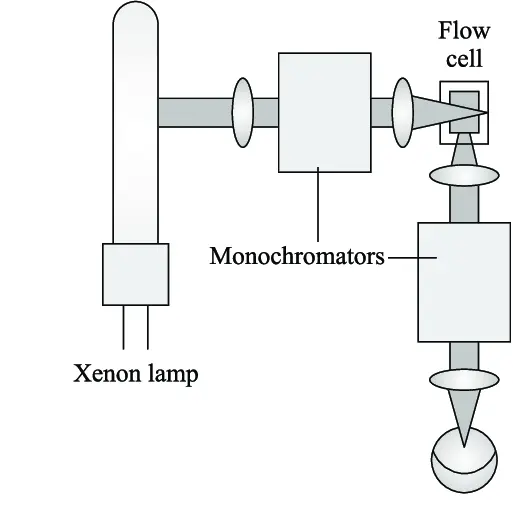
Detection Methods
Accurate detection depends on the chemical nature of the analyte:
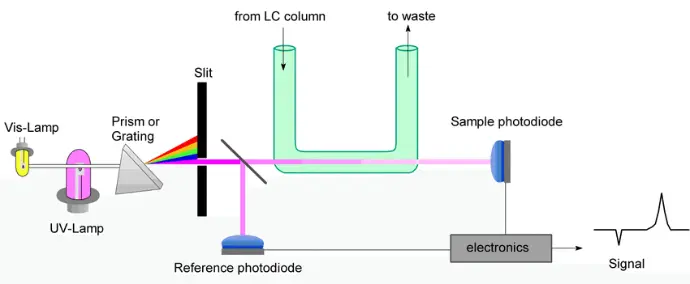
UV-Vis Detectors
Principle: Molecules absorb UV or visible light at specific wavelengths. The detector measures absorbance proportional to concentration.
Advantages:
Universal for compounds with chromophores (double bonds, aromatic rings).
High sensitivity and reliability.
Simple and cost-effective.
Limitations:
Cannot detect compounds without UV-absorbing groups (many sugars, lipids).
Applications:
Pharmaceuticals .
Food industry (dyes, additives).
Environmental monitoring (pollutants).
Troubleshooting HPLC Common Problems and solutions
Even well-trained scientists face challenges in HPLC. Understanding symptoms, causes, and fixes is essential:
Peak Tailing : Caused by column overloading or contamination → Solution: reduce injection volume, regenerate/replace column.
Baseline Noise : Caused by detector instability, bubbles, or poor solvents → Solution: degas mobile phase, check detector lamp, use fresh solvents.
Retention Time Shifts : Caused by mobile phase composition changes, temperature fluctuations → Solution: verify solvent ratios, maintain stable column temperature.
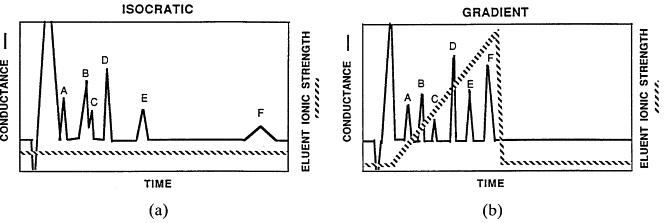
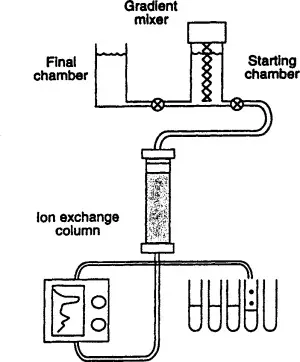
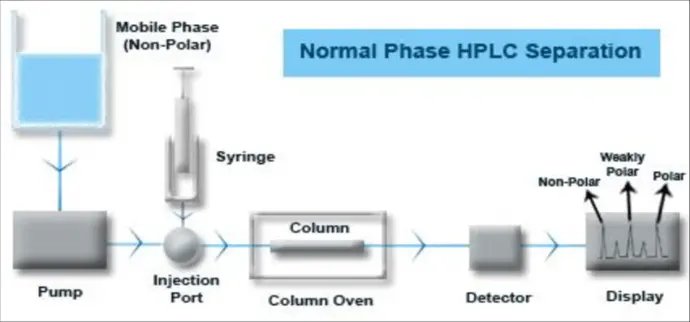
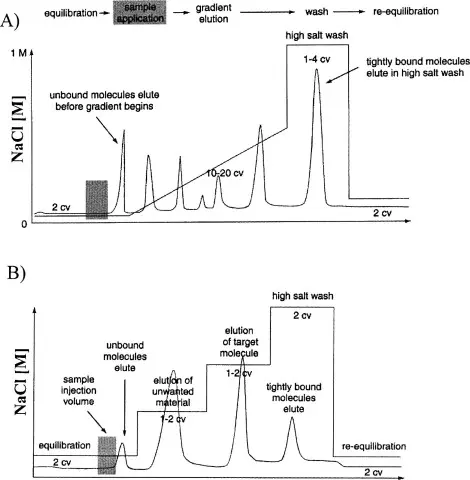
Gradient vs Isocratic Elution
Isocratic Elution
Fixed mobile phase composition.
Simpler, reproducible, cost-effective.
Best for analytes with similar polarity.