High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful analytical and purification technique widely used in chemistry, biochemistry, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. By separating, identifying, and quantifying compounds in complex mixtures, HPLC has become a cornerstone tool in research and industry.
What is HPLC?
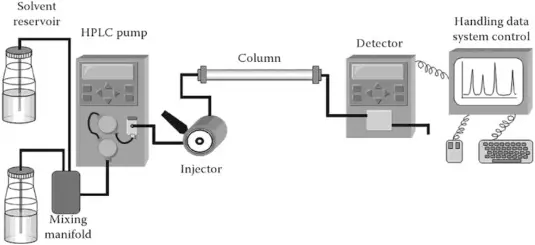
HPLC is a chromatographic technique that separates components of a liquid mixture based on their interactions with a stationary phase (column) and a mobile phase (solvent). Molecules with different chemical properties such as polarity, size, or charge move through the column at different rates, allowing precise separation and analysis.Read more
Key Components of an HPLC System:
Pump: Moves the mobile phase through the column at high pressure.
Injector: Introduces the sample into the system.
Column: Contains the stationary phase where separation occurs.
Detector: Monitors the eluting compounds (UV, fluorescence, refractive index).
Data System: Records and analyzes chromatograms.
HPLC Techniques
There are several HPLC techniques, each designed to separate compounds based on different principles:
1. Normal Phase HPLC
Stationary Phase: Polar
Mobile Phase: Non polar solvents
Application: Separation of polar compounds, natural products, and small molecules.
2. Reverse-Phase HPLC (RP-HPLC)
Stationary Phase: Non-polar (C18 columns commonly used)
Mobile Phase: Polar solvents (water, methanol, acetonitrile)
Application: Widely used in pharmaceuticals, peptides, proteins, and biomolecules.
3. Ion-Exchange HPLC
Principle: Separation based on ionic charge
Application: Purification of proteins, amino acids, and nucleotides.
4. Size-Exclusion HPLC (Gel Filtration)
Principle: Separation based on molecular size
Application: Analysis of proteins, polymers, and biomolecules without denaturation.
5. Chiral HPLC
Purpose: Separation of enantiomers (mirror-image molecules)
Application: Pharmaceutical analysis to determine enantiomeric purity.
HPLC Applications
HPLC has a wide range of practical applications across multiple industries:
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
Purity analysis of drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)
Quantification of drug metabolites in biological samples
Quality control in formulation development
2. Biotechnology and Life Sciences
Separation and analysis of peptides, proteins, and nucleotides
Purification of recombinant proteins and enzymes
Detection of biomarkers in clinical research
3. Food and Beverage Industry
Detection of vitamins, preservatives, and contaminants
Analysis of sugars, amino acids, and natural compounds
Quality control of beverages and functional foods
4. Environmental Analysis
Monitoring pollutants in water, soil, and air
Detection of pesticides, herbicides, and heavy metals
Analysis of industrial effluents
5. Chemical and Natural Product Research
Isolation and purification of plant metabolites
Analysis of synthetic compounds and chemical intermediates
Study of complex mixtures from natural sources
Advantages of HPLC
High sensitivity and precision
Ability to separate complex mixtures
Quantitative and qualitative analysis
Adaptable to small-scale analytical studies and large-scale preparative purification
Conclusion
HPLC is a versatile and indispensable tool in modern science, bridging analytical chemistry and preparative applications. Whether you are analyzing trace compounds in biological samples, purifying pharmaceuticals, or studying natural products, mastering HPLC techniques provides accuracy, reliability, and scalability.
With continuous innovations in column technology, detection systems, and automation, HPLC remains at the forefront of research and industrial applications, making it a fundamental technique for scientists worldwide.
Our latest content
Check out what's new in our company !
